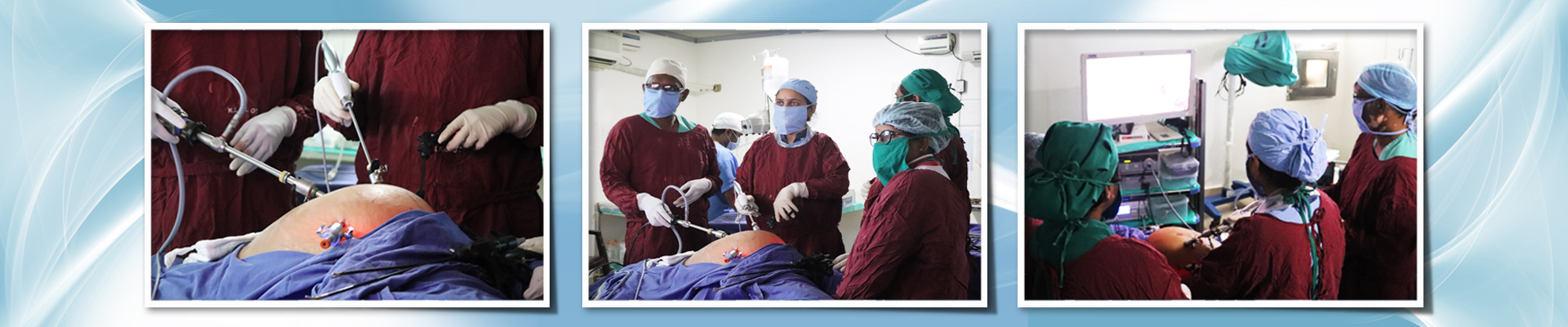
Appendectomy may be performed laparoscopically as an open operation. Laparoscopy is often used if the diagnosis is in doubt, or in order to leave a less visible surgical scar. Recovery may be slightly faster after laparoscopic surgery, although the laparoscopic procedure itself is more expensive and resource-intensive than open surgery and generally takes longer.